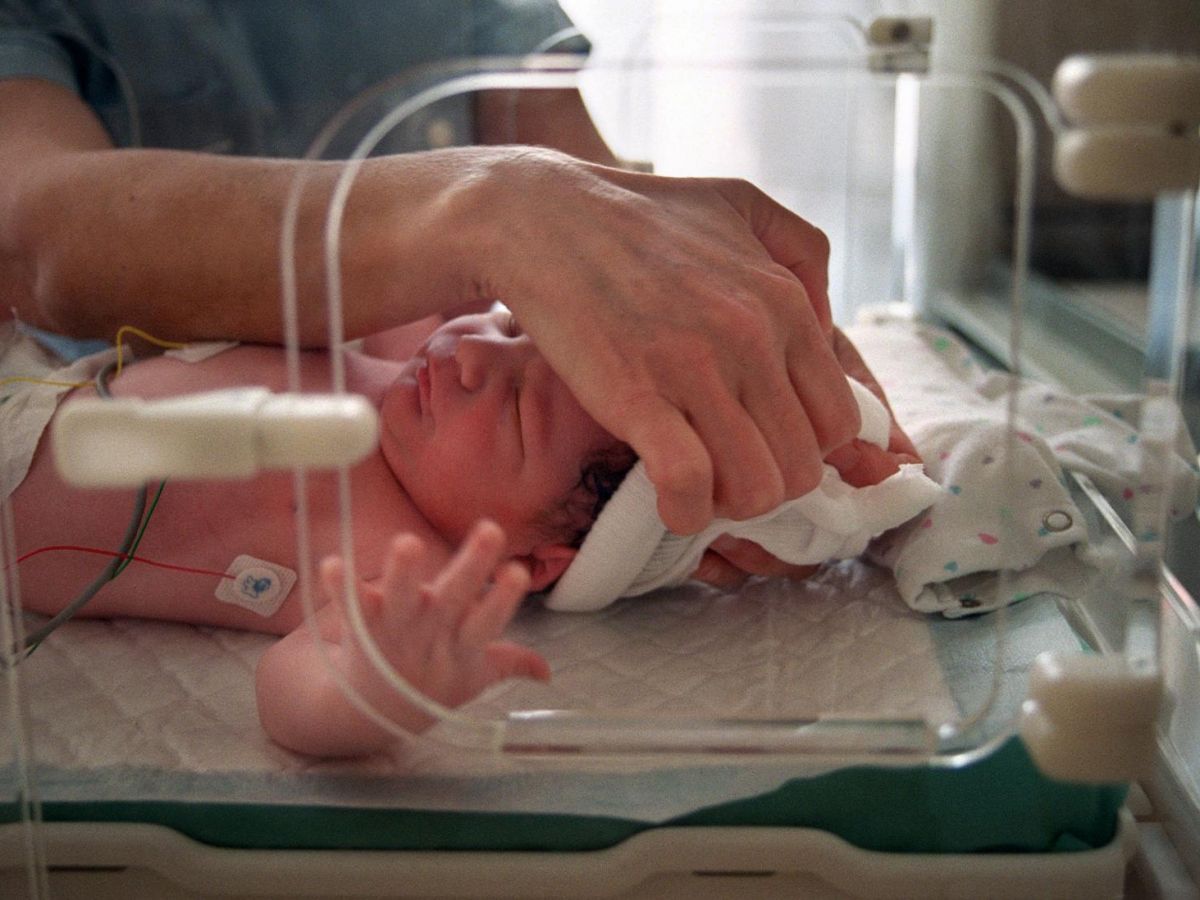
Screening all newborns for treatable genetic diseases is no longer science fiction, shows an American experiment reported in the medical journal The following are some of the reasons why you should consider hiring someone elseYou can also find out more about the Ma. The usual screening three days after birth detects in a drop of blood deposited on a blotter metabolic abnormalities that can be treated with medication or an adapted diet. The recent possibility of sequencing and analyzing in a few days the entire genome of newborns from this same sample has completely changed the situation for finding pathologies of genetic origin.
She convinced American researchers at Columbia University in New York to launch a large-scale genomic screening of 100,000 children. With the parents' consent, nearly 4,000 children have already been tested in one year for genes that cause epilepsy or 156 known and treatable genetic diseases.
110 babies identified by verifying their genome
While only 26 of these children were screened using the traditional method, 110 babies carrying mutations linked to genetic diseases were identified by checking their genome.
These children were often able to receive appropriate treatment, particularly for epilepsy, deafness, dwarfism, long QT cardiac syndrome and severe immune deficiency. Other children were able to have a diet adapted to an enzyme deficiency such as that of G6PD.
Read alsoRare diseases: neonatal screening expands in France
Treat certain diseases early
This pilot project called GUARDIAN was launched in 2022 by American researchers with the financial support of the pharmaceutical laboratory Sanofi, the manufacturer Illumina of DNA sequencers and the genetic testing company GeneDx. The objective is to develop this new mass screening to be able to apply it one day to the 210,000 annual births in the State of New York. After genetic counseling, it will make it possible to treat certain diseases early, which is a guarantee of effectiveness, and to avoid unpleasant surprises or subsequent diagnostic wandering for parents.
Used in addition to traditional biochemical screening, genomic screening will develop taking into account the growing discoveries in medical genetics. Generalized neonatal genetic screening is also being evaluated in France within the European framework of the SCREEN4CARE project and such screening of 100,000 newborns has already started in the United Kingdom with the Generation Study program.