Over the last decade, medicine has seen an increasing focus on integrating different disciplines that seek to understand the human being as a whole. In this context, integrative medicine has acquired particular importance. How are the mind, the immune system and the muscles intimately linked? How do these interactions influence general health, aging and chronic diseases?
One emerging topic is how chronic low-grade inflammation can influence muscle wasting and brain deterioration, and how a PNI-based clinical approach can provide answers to these health problems.
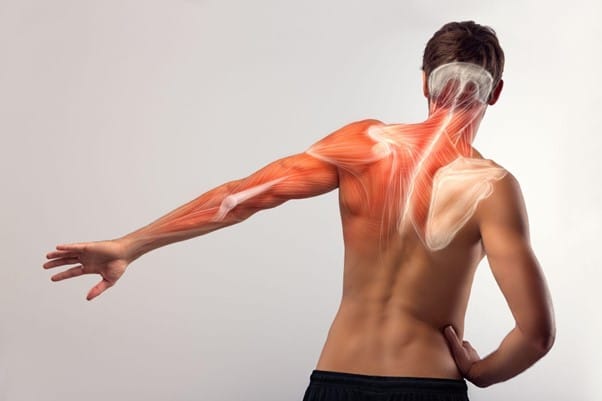
Skeletal muscle: more than just an organ of movement
THE skeletal muscle represents 40% of the total body mass and is essential for movement, posture and body heat regulation. But its function goes far beyond the mechanical. Recent research has identified that skeletal muscle acts as an endocrine organ releasing molecules called myokines during muscle contraction.
These myokines have systemic effects, meaning they affect other organs, such as the brain. This is particularly relevant in the context of physical exercise, since myokines released during physical activity can have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, promoting not only physical health, but also mental health.
In pathological situations, such as chronic low-grade inflammation, skeletal muscles suffer from wear and tear and dysfunction. This phenomenon, known as sarcopenia, affects not only mobility, but also brain health and can accelerate cognitive decline. But how exactly does this interaction between skeletal muscles and the brain occur? To better understand it, we must first talk about chronic inflammation.
Chronic low-grade inflammation: the silent enemy
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injuries or infections. However, when inflammation persists chronically, Even at low levels, it can trigger a range of serious health problems. It has been linked to diseases such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. In the context of psychoneuroimmunology,
silent or low-grade chronic inflammation, affects communication between the immune system, brain, and skeletal muscles. This process feeds on itself, creating a vicious cycle in which chronic inflammation not only causes muscle deterioration, but can also negatively affect the brain, impairing cognitive and emotional functions. Why is psychoneuroimmunology gaining relevance in health?
Psychoneuroimmunology is an interdisciplinary field that has grown rapidly in recent decades. This science studies how
nervous, endocrine and immune systems interact with our emotions and behaviors. PNI is essential for understanding how stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors influence the development and progression of chronic diseases. Integrative medicine seeks to combine conventional therapies with alternative and complementary approaches to improve health. This type of medicine does not focus
only on the treatment of symptoms,but rather on identifying and treating the underlying causes of discomfort or disease, based on a holistic view of the human body. From the approach of
integrative medicine and psychoneuroimmunology, there Skeletal muscle health is crucial to maintain the body's balance. This tissue is not only essential for movement, but also plays an endocrine role that directly affects brain function and the immune system. Therefore, understanding the relationship between muscles, inflammation, and mental health is essential in the context of integrative medicine. Impact of inflammation on skeletal muscle
When
skeletal muscle is exposed to a state of chronic low-grade inflammation, The muscle’s ability to regenerate and maintain health is significantly reduced. Inflammation interferes with muscle protein synthesis, leading to muscle atrophy. This muscle wasting not only affects mobility and strength, but also has implications for the individual’s overall health, increasing the risk of falls, fractures, and dependency. Impact of inflammation on the brain
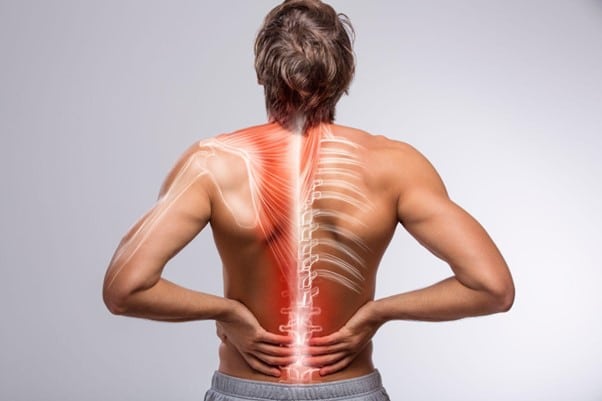
On the other hand, inflammation also affects the brain. Neuroinflammation, which is inflammation of the central nervous system, is associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and depression. Chronic inflammation can impair communication between neurons and compromise the production of neurotrophic factors such as BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor), which is essential for the growth and maintenance of neurons.
In this sense, skeletal muscle and the brain are victims of the same enemy: chronic low-grade inflammation. There are, however, ways to counteract these effects, and this is where psychoneuroimmunology and exercise science come into play.
Physical exercise: the great ally against inflammation
One of the
pillars of integrative medicine and clinical PNI East physical exercise. Skeletal muscle contraction during exercise is not only an effective tool to combat chronic low-grade inflammation, but also improves communication between muscle and brain. When the muscle contracts, it releases exerchins, a special type of protein that has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. These exercises can improve brain health by reducing neuroinflammation and stimulating the production of BDNF, which promotes neuroplasticity and improves cognitive performance.
Benefits of Exercise for Brain Health
Various studies have shown that regular exercise can improve memory, attention, and mood. In older adults, exercise has been shown to help delay cognitive decline and reduce the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases.
In addition, exercise has an antidepressant effect. Myokines and exerkines released during physical activity not only act on muscles, but also cross the blood-brain barrier and exert effects on the brain, improving mood and reducing symptoms of depression.
The Future of Integrative Medicine
Psychoneuroimmunology and integrative medicine are revolutionizing our way of understanding health. We can no longer see the body as a collection of isolated parts; each system is interconnected and mental, physical and emotional health are sides of the same coin. Understanding the communication between the brain, immune system and skeletal muscle opens new avenues for the treatment of chronic and neurodegenerative diseases. In this context, physical exercise, combined with adequate stress management and anti-inflammatory nutrition, is presented as a powerful therapeutic tool in the fight against chronic low-grade inflammation, sarcopenia and brain deterioration. Clinical PNI will continue to play a vital role in the research and development of new therapeutic approaches that promote holistic and sustainable health.
Your certified training at the best price!!