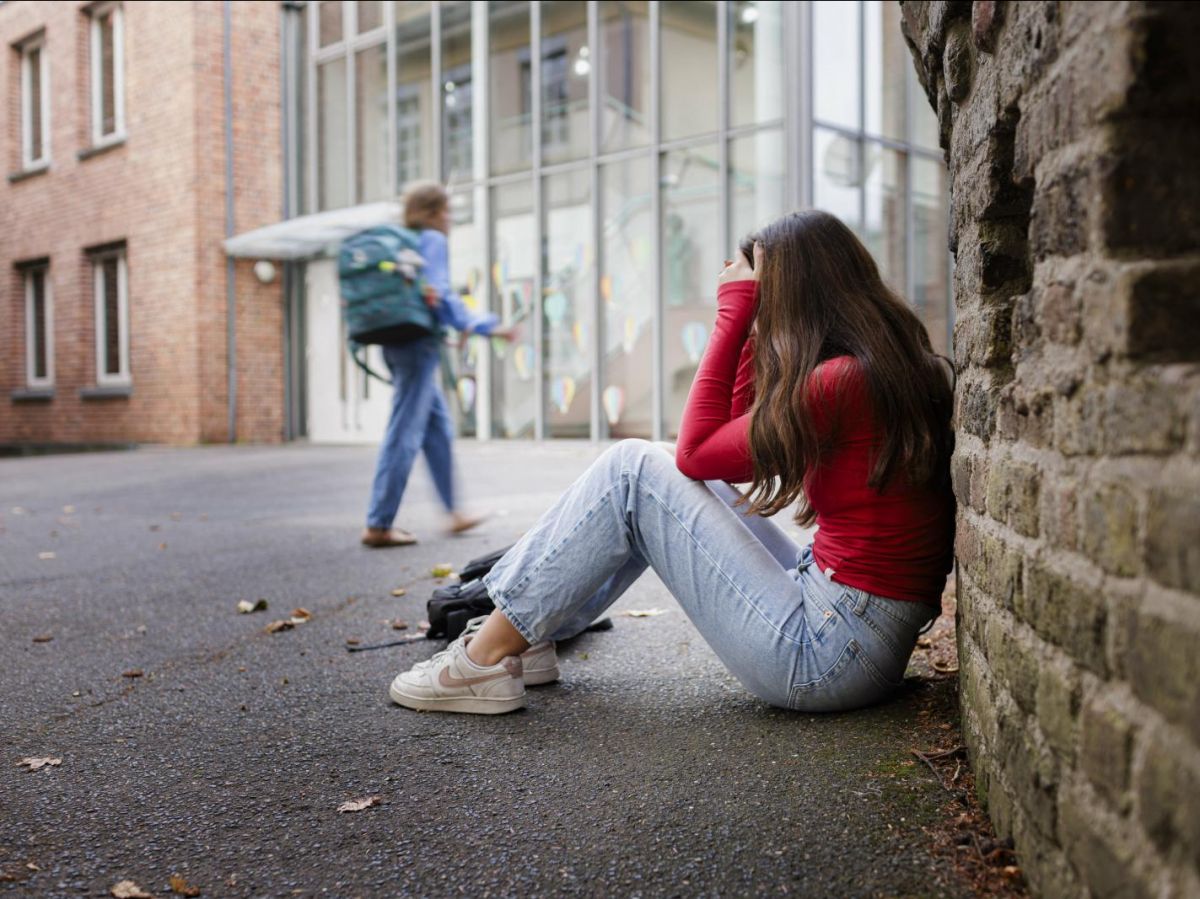
"Nobody spoke to me."
"They called me 'the intellectual'"
“My parents understood when I came home from school with a swollen lip.”
Read alsoFrance: More than one in 10 children suffers from at least one mental health disorder
In France, 5% of primary school children and 2% of high school and middle school students said they were “afraid of going to school” in 2023, according to a government investigationWorldwide, one in three students (32%) reports having been bullied at school at least once in the last month, according to a report by UNESCO of 2019. Although common, this experience of school bullying is far from trivial and has harmful effects in the long term, demonstrates a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience. “ Our study was the first to measure what happens acutely in the brain during an act of harassment.", explains to Science and Future Lauri Nummenmaa, a neuroscientist at the University of Turku (Finland), who led this work.
A brain response in regions linked to emotional distress
Read alsoCyberbullying causes eating and psychological disorders in both the bullied and the bullied
In a functional MRI machine, which allows the activation of brain areas to be monitored in real time, 51 adolescents and 47 adults watched nine-minute videos. Each simulated a bullying situation in the first person, that is, from the victim's point of view. Teases, intimidation, and mean pranks were acted out with young actors. Bullying mobilized large-scale brain networks in the brainstem, amygdala, thalamus, and somatosensory and motor cortices", lists Lauri Nummenmaa. " These regions are known to support the processing of emotional and social distress as well as tactile and motor functions, the latter likely related to fight-or-flight readiness during bullying.. »
A “state of mass alert”
Read alsoPornographic Deepfakes: A Wave of Cyberbullying Against Women in Politics
The consequences of bullying can be serious. Children who have experienced it are twice as likely to suffer from loneliness, insomnia, and suicidal thoughts, the UNESCO report states. In this new work, the researchers observed weaker responses to bullying videos in areas of the prefrontal cortex associated with emotion regulation in subjects who had experienced it in the past. Furthermore, in all participants, the simulation of hostile situations reduced the time they spent looking at the same area of the image compared to videos of positive interactions, suggesting an aversion to watching bullying. We were surprised to see how strong the effects were and how consistently the brains of adults and adolescents responded“, reports Lauri Nummenmaa.
For the researcher, the most important conclusion is the extent of the massive state of alert that harassment causes in the brain.. "Repeated activation of this distress circuit and its somatomotor components is likely to be detrimental to psychological and somatic well-being“, supports Lauri Nummenmaa. “ School bullying is associated with alterations in affective stress and emotion regulation systems, likely reflecting adaptation to and management of stress.. »
HARASSMENT RESOURCES. Spread across France, 150 academic and departmental harassment managers are responsible for supporting families until the situations are resolved. Their contact details are available on the Ministry of Education website (at the bottom of the page).